We have come to appreciate the many roles Honey Bee’s play in our agriculture world, Beekeepers Apiary and our health. Commercial Beekeepers work closely with AG Framers to pollinate and subsequently increase Fruit, Nuts and Vegetable corps for the masses. Hobbyist, Homesteaders and small-scale Beekeepers capitalize on Honey Bees natural foraging ability to harvest variety of Honey flavors from flower, herbs, spices, and fruit to supply raw, unfiltered natural Honey to the local community.
Honey Bees influence an important and often overlooked aspect of our food system: the interconnectedness of honey bee health, agricultural practices, and human well-being. Here’s a breakdown of these connections and their implications:
- Honey Bee Health and Human Health:....
- Honey's Benefits: Honey is not only a natural sweetener but also contains beneficial nutrients and compounds that can contribute to human health and well-being. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties have been recognized for their positive effects on health.
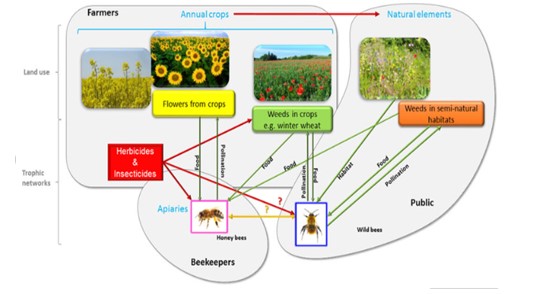
- Impact of Pesticides: The health of honey bees is closely tied to the safety of the crops they pollinate. Pesticides, especially neonicotinoids, insecticides, and herbicides, can have severe consequences for bee colonies. These chemicals are absorbed by plants and can be transferred back to the hive through pollen and nectar.
- Effects of Pesticides on Bees:
- Colony Collapse: Exposure to harmful chemicals can lead to colony collapse disorder (CCD), where entire bee colonies die off or become severely weakened. This collapse not only threatens bee populations but also disrupts the pollination services that bees provide.
- Impact on Agriculture and Food Supply:
- Decreased Crop Yields: With fewer bees to pollinate crops, agricultural yields can drop. This reduction in crop productivity can lead to shortages and increased prices for fruits, vegetables, and other crops.
- Economic Consequences: Lower crop yields can create a ripple effect, causing fluctuations in grocery store supply and demand. This, in turn, can lead to higher prices for consumers and economic challenges within the agricultural sector.
- A Call for Sustainable Practices:
- Protecting Pollinators: To ensure the health of honey bees and, consequently, our own health and food security, it’s essential to adopt sustainable agricultural practices. This includes reducing or eliminating the use of harmful chemicals, promoting organic farming, and supporting pollinator-friendly practices.
- Supporting Beekeepers: Encouraging and supporting both commercial and hobbyist beekeepers can help maintain healthy bee populations and ensure that the benefits of honey bees extend to our food supply and overall well-being.
Conclusion: The health of honey bees is fundamentally linked to human health and food security. By addressing the use of harmful chemicals in agriculture and supporting practices that protect bees, we can promote a healthier environment and a more stable food supply. Recognizing this connection is crucial for fostering sustainable practices that benefit both our ecosystems and our daily lives.